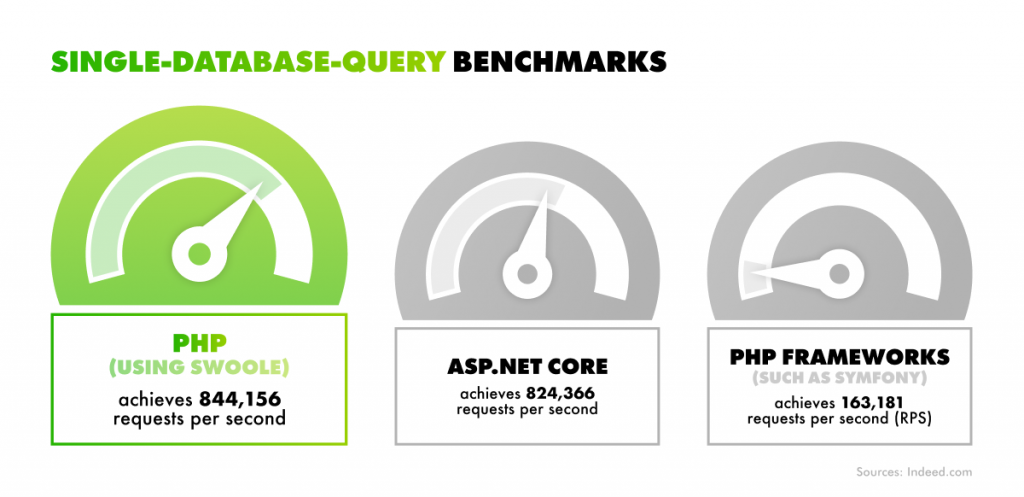
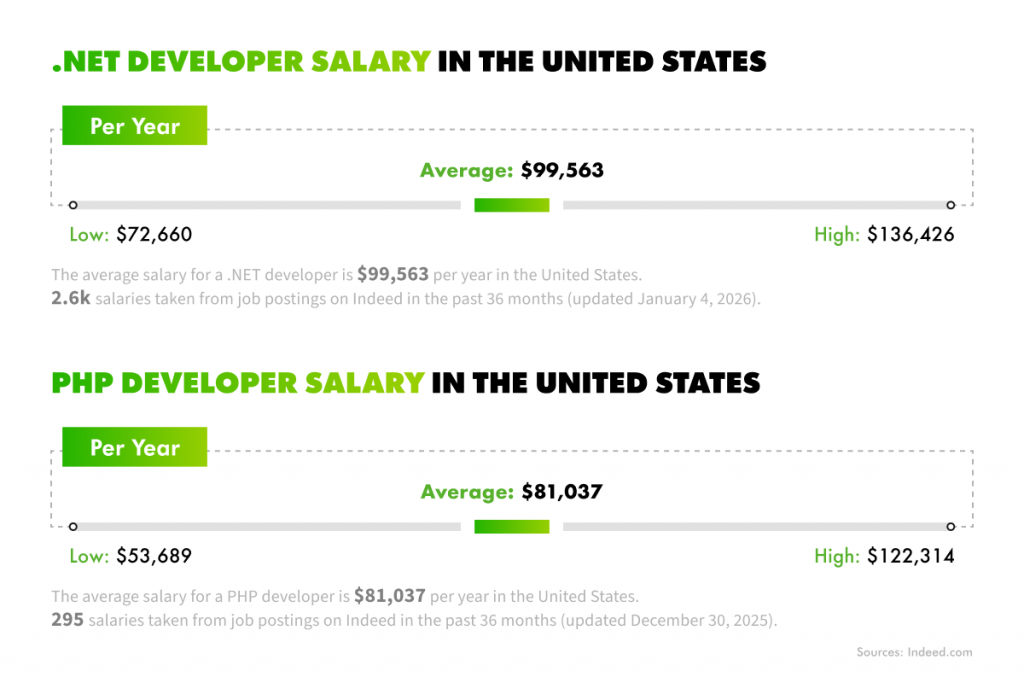
The choice between PHP and ASP.NET would seem to be relatively straightforward on the surface and complicated the moment you look at real data. PHP powers around 73% of all websites with a known server-side language. Yet, from a developer perspective, the ASP.NET ecosystem is among the most widely used back-end technologies today. According to Statista and Stack Overflow, ASP.NET Core is used by nearly 19,7% of professional developers, with classic ASP.NET adding another 14,2%.
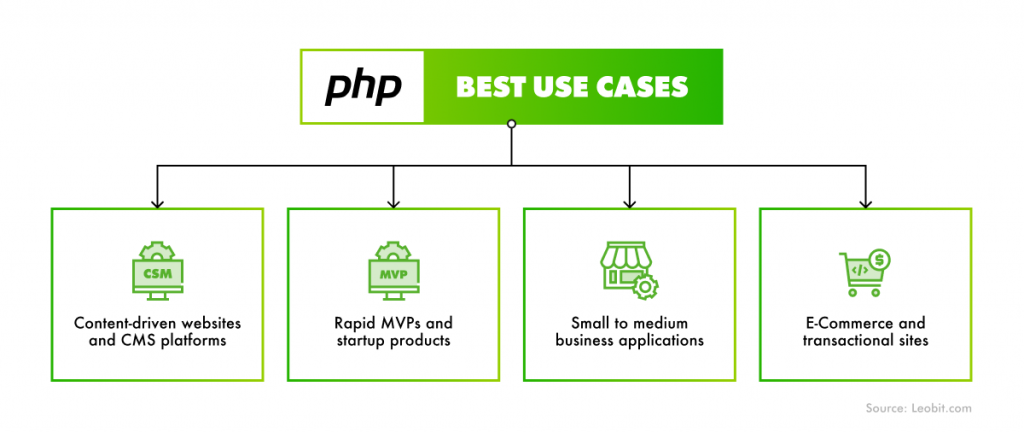
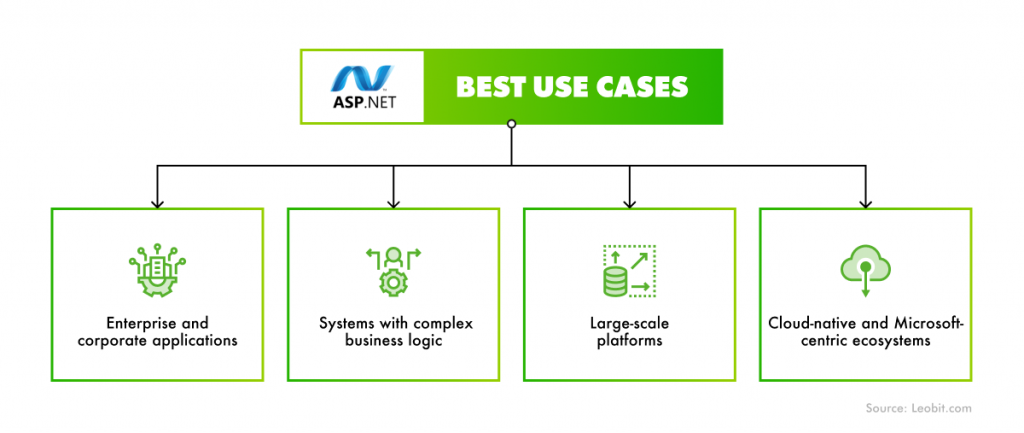
PHP dominates by deployment numbers, largely due to its deep roots in CMS-driven and legacy systems. On the other hand, ASP.NET gains ground in modern custom web development, especially in enterprise software, SaaS platforms, and native cloud applications. This contrast is at the heart of the PHP vs. ASP.NET debate.
In this article, we’ll compare PHP and ASP.NET through a business lens to understand why both technologies still matter, where each one performs better, and how their differences affect real business decisions.
But before that, let’s take a closer look at what each of these technologies offers.