It’s not easy to be compliant in healthcare. Especially if you are a healthcare application development provider accountable for secure data processing and storage.
You must follow a range of stringent regulations and healthcare data security standards, including HIPAA, FHIR, and others. Otherwise, a healthcare organization that will adopt your software may be penalized.
Those who fail to meet data standards in healthcare may be fined up to $50,000 US dollars per civil violation. For a more serious offense, like selling PHI data, an offender may get a 10-year jail sentence.
An Illinois-based healthcare network is famous for the largest HIPAA settlement that resulted in a $5.5 million penalty. Because of insufficient risk analysis, the data of four million people was compromised. A dear price for the lack of physical and administrative safeguards, isn’t it?
To save your nerves and reputation, Leobit’s team has prepared an overview of top healthcare regulations and compliance rules. Let’s talk about building HIPAA compliant software, HL7 standard, and other data standards in healthcare:
- What does HIPAA mean for a healthcare application development provider
- FHIR and HL7 data exchange standards in healthcare
- Other data standards in healthcare to watch out for (ICD-10, XDS/XDS-I, and EVV)
What Does HIPAA Mean for a Healthcare Application Development Provider
HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. It is a US legislation signed on August 21, 1996, to implement data security provisions that protect patients’ medical information. HIPAA regulates the processing of protected health information (PHI) by any organization working on the US market.
Therefore, when healthcare application development providers design solutions that require medical data processing, they have to follow HIPAA. Only HIPAA compliant software will allow their customers to observe the law.
A Medical App Must Meet HIPAA Compliance Software Requirements:
- If a medical app is used by the entity or business associate, that must be compliant. The entities covered in HIPAA include most healthcare providers (doctors, hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and pharmacies), healthcare plans, and healthcare clearinghouses. Business associates are organizations that collect, process, store, or transmit PHI on their behalf. For example, if you launch a telemedicine app to offer remote treatment, you must meet HIPAA compliant software requirements. Here, both doctors and hospitals are the covered entities.
- If a medical app accesses, produces, or stores protected health information (PHI). Personal health information is any information about health status, provided care, or healthcare payments linked to a specific person. Medical information becomes PHI only when it includes personal details, like names, addresses, dates, contact information, etc.

For example, if an application has an electronic-health management feature and enables clinicians to track patients’ progress, it must be compliant. This solution will store confidential information of different individuals linked to their treatment history.
Hence, before racking your brains about reaching HIPAA compliance, clarify whether you need it. First, analyze what kinds of data you will process. Second, think about who will use this tool and what for.
You can read about the best practices in healthcare application development in our previous article.
If you create software for one of the HIPAA covered entities and/or deal with protected health information, mind HIPAA software requirements. Let’s discuss the key provisions of the HIPAA Security Rule below.
Mandatory HIPAA Safeguards for HIPAA Compliant Software Development
Fortunately, the creators of HIPAA clarified every aspect of the compliance. The HIPAA Security Rule lists all the technical, physical, and administrative safeguards that must be implemented. If you have them in place, you can sleep peacefully without worrying about HIPAA compliance.
Note you can choose any means to provide these safeguards.
Technical safeguards
Technical safeguards are something you as a software developer should focus on. Without them, a healthcare organization that will later use your application won’t be able to comply.
| Safeguard | How to implement |
|---|---|
| Access controls | An engineering team must implement procedures that allow only authorized users to access PHI. For example, you can use a password, PIN code, token, key, or biometric data, such as fingerprints and voice |
| Audit controls and activity logs | To track what’s happening with PHI, a compliance app must log all actions. Thus, it’s important to implement hardware, software, and/or procedural mechanisms that record activities in the system and audit them |
| Integrity controls | HIPAA healthcare regulations and compliance require software providers to use procedures that protect data from damage or changes. It’s necessary to identify all authorized and unauthorized access attempts and develop the integrity policy |
| Data transmission security | Healthcare software must support technical security measures that prevent unauthorized access while PHI data is transmitted |
Physical safeguards
These safeguards are related to physical access to ePHI, such as a place of storage, workstation, and smartphone security. They must be implemented jointly by the tech team working on the healthcare solution and the organization that uses the app.
| Safeguard | How to implement |
|---|---|
| Facility access control | Only authorized people should have physical access to the facilities of a covered entity |
| Workstation and device security | A covered entity must restrict the use of workstations and mobile software that have access to PHI. Video surveillance, door and window locks, security system, and data deletion from mobile devices after employees leave the facility are the most popular ways to do this |
Administrative safeguards
These safeguards dictate healthcare organizations that use HIPAA compliant software how to manage it. Overall, they need to assign a security officer, analyze risks and limit access.
| Safeguard | How to implement |
|---|---|
| Information access management | Covered entities should ensure “minimum necessary” use and disclosure of PHI. The staff will access PHI only when it needs this data to provide services. Therefore, a healthcare application development team that works on the software has to build it with flexible access controls |
| Risk analysis | For HIPAA compliance, it’s necessary to identify how PHI is processed and analyze potential risks. A healthcare software development team provides a software owner with a clear understanding of data usage practices |
| Security personnel and training | After the software is launched, covered entities must designate a security official and regularly train their staff on how to recognize a cyber attack |
| Data security assessment | A covered entity must perform periodic security checks. This is necessary to make sure the security level meets HIPAA software requirements |
As a healthcare software development provider, you are mainly responsible for the technical part of HIPAA compliant software development. But you can help the covered entities with other aspects. Physical and administrative safeguards depend on technology and HIPAA compliance software vendors. If a software solution processes medical data securely, it will be easier to implement other safeguards.
FHIR and HL7 Data Exchange Standards in Healthcare
In the US, around 1500 million data breaches happen annually. Out of this number, a large share of attacks target healthcare data. According to HIPAA Journal, in 2020, from 400 thousand to over 9,7 million healthcare records were compromised every month.
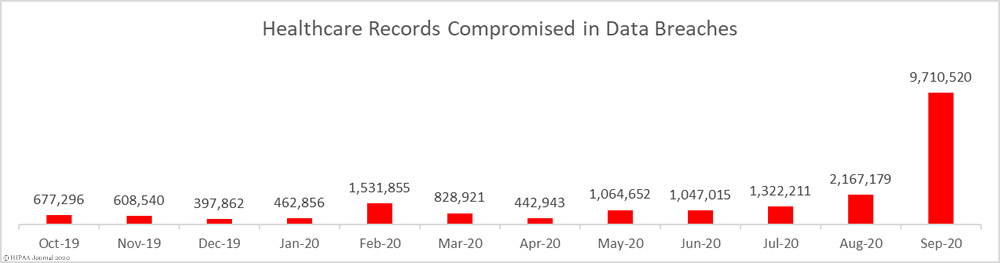
(Source)
Even though HIPAA healthcare regulations and compliance help to protect software from intervention, also follow healthcare data security standards. FHIR and HL7 are the key standards to remember during healthcare software development.
What are HL7 standards and FHIR standard?
HL7 (Health Level Seven) is a set of international standards established to control electronic medical data management, exchange, and integration. They determine how to transfer clinical data between software applications used by healthcare organizations.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standard appeared as an alternative to existing HL7 interfaces standards. But developers and end-users faced operational difficulties caused by the use of HL7v3. Since the HL7 standard was complicated to work with, it was necessary to create something with the same functionality but simpler. That’s how the HL7 FHIR standard was born.
The FHIR standard has better interoperability than the previous versions of HL7, the healthcare standard. In FHIR software, all resources have a common set of metadata, definition, representation method, and a readable part. The system must be securely interpreted by any other software and read by any device type.
As the transition to FHIR has only started, currently, both FHIR and HL7 software standards are used in healthcare software development.
Contact Leobit to discuss your healthcare development needs.
Why should you follow the HL7 standard and FHIR standard?
HL7 healthcare standards, including FHIR, enable healthcare service providers to maximize the benefits of modern technology. To understand in what way, let’s imagine a situation.
When a physician diagnoses a patient and assigns treatment, the doctor needs to access multiple electronic systems. If the services don’t follow the same interoperability FHIR and HL7 software standards, the risk of mistakes is high. The physician may fail to receive the necessary data and misinterpret the information because of missing standardization.
Healthcare regulations and compliance with HL7 interface standards allow software providers to integrate solutions. This optimizes the work of physicians and enhances the quality of care.
Therefore, FHIR and HL7 software standards act as a bridge between modern healthcare services and advancing information technology.

Other Data Standards in Healthcare to Watch Out For (ICD-10, XDS/XDS-I, and EVV)
HIPAA and HL7 healthcare requirements are the main healthcare regulations and compliance standards to follow. But your healthcare application can also become more secure and interoperable if you use other measures.
Here is an overview of other critical standards.
- The ICD-10 is a disease classification coding system. It is aimed at building an infrastructure that would help to create a nationwide health care system where hospitals, clinicians, laboratories, and pharmacies can securely share the same patient data. The ICD-10 initiative appeared as an update to the ninth edition of the international classification of diseases (ICD-9). ICD-10 has more categories than ICD-9 and is a must-follow standard for modern healthcare compliance software and medical apps.
- XDS (cross-enterprise document sharing) is an interoperability profile that describes how healthcare enterprises should share medical information with peers. The main idea is that patient information is provided from the source system. Then, the medical documents are indexed in a registry with a set of specific attributes. A clinician who needs to assess a document can search the index and retrieve the necessary information from the repository.
- XDS-I is an extension to the XDS protocol created specifically for sharing medical images. When XDS-I is used, the XDS repository has only basic information on image series. The retrieval of full-quality images is performed directly from source PACS to the workstation with web-safe methods.
- EVV (electronic visit verification) is a requirement to verify home medical visits with healthcare compliance solutions. The software must check the type of provided service, who receives it, when, where, and for what period. Such checks are usually implemented with GPS tracking and telephone-based systems. Usually, you will need to meet EVV requirements to develop personal care software.
The need to meet these standards depends on the functionality of your app. Therefore, before you implement any new feature, learn the related standards and take care of compliance.
Final Thoughts on Healthcare Regulations and Compliance
Starting work on an EHR, telehealth solution, healthcare compliance software, or any other compliance apps, you must know the rules.
Otherwise, you will need to assemble a team with the relevant experience or hire a software development vendor. Whereas in-house recruitment takes a lot of time, outsourcing enables you to initiate HIPAA compliant software development as soon as you find the right company.
Leobit is an outsourcing company skilled in developing compliant healthcare software. Since we have completed multiple healthcare projects for customers from the US and Europe, e.g., the app for booking hospital appointments, we know what regulations affect different markets.












