Millions of web apps exist to assist businesses in delivering services and stuff. Web apps are the best solutions for connecting with consumers and increasing user engagement.
When it comes to web development, though, you must choose between single-page applications (SPAs) and multi-page applications (MPAs).
This article will explain their benefits and drawbacks to assist you in deciding which one to use for your project.
Intro
There are two broad techniques for designing web apps: single-page and multi-page. However, perspectives on their advantages and downsides differ significantly, and there is still some uncertainty regarding which strategy to use for designing applications.
While single-page and multi-page apps are conceptually similar, there are differences between the two web applications.
What is a single-page application, and how does it work?
A single-page application is a web application that engages with the browser by continuously modifying the existing page with new data from the server, instead of the browser loading complete new pages.
A single-page program is not constrained to one page. Users view different SPA areas as separate pages as they move across them. However, those aren’t other web pages; they’re called views and are activated by JavaScript. Unlike MPAs, where each page has its shareable link, views in SPAs do not have dedicated links unless you modify the code slightly.
After the initial page loads in a SPA, all interaction with the server occurs via AJAX requests. These AJAX requests return data rather than markup, often in JSON format. The software uses JSON data to dynamically change the website without refreshing it.
All UI interaction in a pure SPA happens on the client side, using JavaScript and CSS.
What are the benefits of SPAs?
Let’s look at why a single-page app architecture can be the best option for your project.
Seamless UX
Single-page applications are appealing because they give users a linear experience. SPAs load only the complete content when you click on a tab. These applications also provide superb scrolling functionality that allows users to explore effortlessly. It has parallax scrolling, which produces a transition effect on applications.
Easier development
Several elements streamline SPA development.
- Backend and frontend components may be built concurrently, which speeds up development processes.
- A single-page app is easier to deploy because it provides a single HTML file with a CSS and JS bundle.
- A SPA is typically built using popular frameworks (React, Vue.js, AngularJS) with debugging tools based on Chrome, such as Vue.js DevTools.
What are the drawbacks of SPAs?
Despite being appealing to customers, single-page applications have their own set of issues that might hinder your desired outcomes, whether it’s receiving enough targeted traffic or conversions.
Trickier search optimization
Google prefers lengthier content that includes relevant keywords about any product or service. JavaScript is not selected by search engines, and SPAs are developed with JavaScript frameworks. Every web program in JavaScript loads data without the page being refreshed and only when the user requests it. This indicates that there are no specific URLs optimized for search engines, and the material is not visible to search engines. The problem can be solved entirely by server-side rendering.
No direct access to analytics
Single-page apps are more difficult to track and measure against essential metrics. Traditional tracking code, such as that found in Google Analytics, or similar applications, will not work here. However, this does not exclude you from tracking any data; many methods are available, from dedicated plugins and real-time user monitoring tools to GTM triggers.
Security issues
Cross-site scripting causes a security issue in single-page applications. Hackers can use sensitive data on a web page to insert harmful code. The situation, though, is controllable. Furthermore, automated testing is quite challenging due to the application’s dynamic nature.
JavaScript support requirement
Users cannot use the app to its full potential if they disable JS in their browser. Some experts argue that all websites and online apps should deliver a functioning version to visitors who have JS disabled or do not receive an appropriate JS experience.
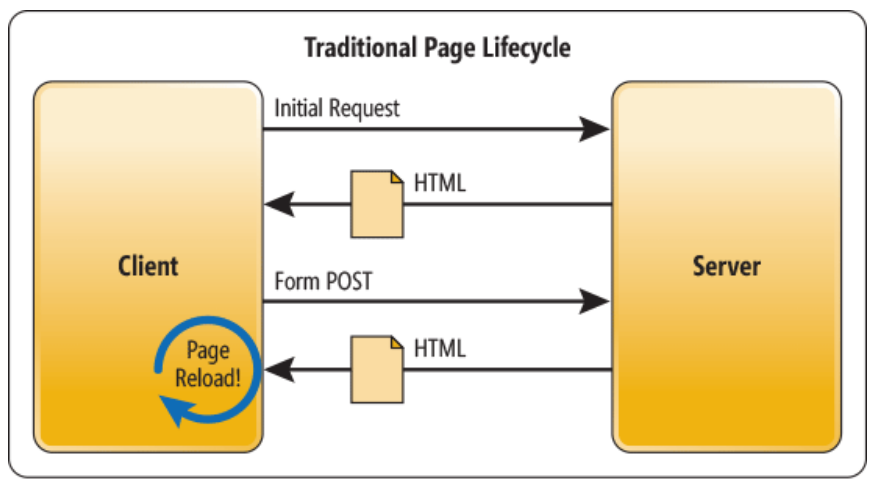
What is a multi-page application, and how does it work?
A multi-page app (MPA) is a standard web application that runs on a server. Every time a user refreshes a page or moves from one page to another, the browser requests data from the server.
MPAs, as the name implies, have numerous pages that work independently at all levels: in development, in the eyes of real users, and the eyes of search engines. HTML is used for basic functionality, CSS for style, and JavaScript for interactive features in most current MPAs. A multi-page application is any primary e-commerce site, such as Amazon, that contains several categories and pages and static and interactive parts.
What are the benefits of MPAs?
Even though SPAs are frequently described as competitors to MPAs, the former is unlikely to drive the latter away. Both techniques are appropriate for certain corporate goals. Let’s go through the main benefits of classic, multi-page apps.
Scalability
This architecture type lets you create as many new pages as you like for each product or service and make modifications to them. This scalability is essential for large e-commerce businesses or programs that handle extensive data.
Easier search optimization
Mobile and web application development companies want their service page to appear on the first page of a search engine. It is simple to construct a sitemap for an MPA, advise search engines to follow or ignore specific pages or links, and support the site’s structure with internal linking. Because an application may be optimized for one keyword per page, it increases the possibility of ranking for several keywords.
Easier access to analytics
MPAs make it simple to integrate with Google Analytics. It is required for vital information about your page’s visitors. That way, you’ll know which pages are performing well and what your visitors enjoy about your website. After analyzing this, you may create several new adjustments to the website and other fields that require development.
What are the drawbacks of MPAs?
Since no approach to web development is flawless, strategies evolve, and new tools, frameworks, and solutions emerge regularly. Consider what you could give up if you choose an MPA method.
Longer loading times
Multi-page applications are slower than single-page apps. Every time a user clicks on a tab, it reloads. When there is an action, resources such as CSS, HTML, and Script are refreshed. As a result, both speed and performance suffer.
More complex development
Developers begin coding from the base up for both the front and back end. Furthermore, some issues may be with separating the front and back end. As a result, it takes longer to develop.
Choosing between multi-page and single-page app architecture
There is no proper answer as to which architecture is superior because everything relies on the web app features you intend to design and the jobs the app should do. Customers should base their decision on their commercial demands and the technical requirements of a particular project.
A multi-page application is a good solution if your website displays many items or services, and SEO is vital for attracting clients.
Suppose you want to give maximum functionality in little webspace, establish a dynamic platform, or flexibly manage vast volumes of data. In that case, a single-page app is your most suited solution.














